Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and Polysaccharides are the three major categories of carbohydrates. This categorization is based on the number of sugar unit. Let’s see the differences between them.
Differences between Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and Polysaccharides
| Monosaccharides | Disaccharides | Polysaccharides |
| Single sugar unit present in structure. | Two sugar units present in structure. | Multiple sugar units present in structure. |
| No glycosidic bond present. | Single glycosidic bond present between the sugar units. | Multiple glycosidic present in the structure. |
| Low molecular weight. | Higher molecular weight than the monosaccharides. | Very high molecular weight due to long chain of sugar units. |
| Can not be hydrolyzed. | Can be hydrolyzed into two monosaccharides. | Hydrolyzed into multiple monosaccharides. |
| High reactive in chemical reaction due to simple structure. | Moderate reactive in chemical reaction. | Low reactivity due to complex structure. |
| Directly enters glycolysis for energy release. | Broken down into monosaccharides before entering into metabolic pathway., | Generally stored as starch or glycogen and broken down when needed. |
| Highly soluble in water. | Soluble in water. | Less soluble and form colloids with water. |
| Provide quick and short term energy. | Energy released moderately. | Provide slow and sustained energy. |
| Directly absorbed into bloodstream. | Firstly, broken down into monosaccharides and then get absorbed. | Broken down into simple sugar before digestion. |
What are Monosaccharides in Biochemistry?
Monosaccharides are simplest category of carbohydrate. These are also known as simple sugar with the general formula of Cn(H2O)n.
Due to single sugar unit monosaccharides cannot be further hydrolyzed or broken down into simple sugar. Some common examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose and galactose etc.
Characteristics:
Here are some basic characteristics of monosaccharides.
- Composed of one sugar unit.
- Generally sweet in taste.
- Monosaccharides are absorbed quickly in bloodstream.
- They provide instant and short-term energy.
What are Disaccharides?
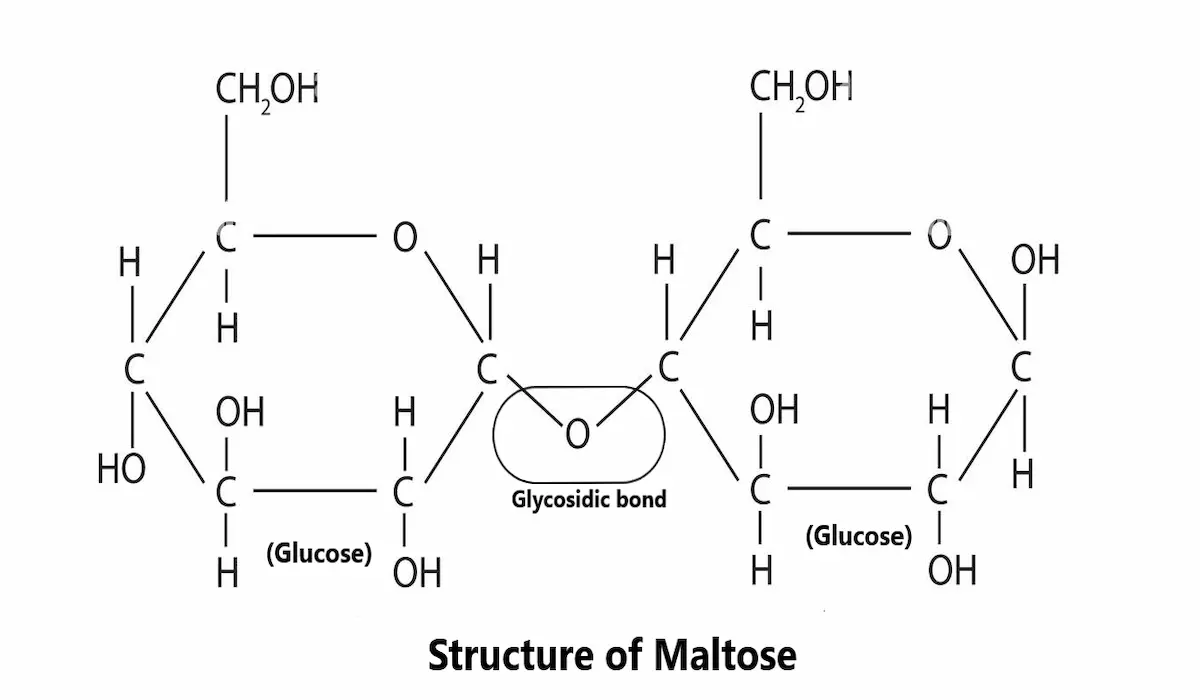
Disaccharides are a group carbohydrates composed of two monosaccharides units or two sugar units. These monosaccharides or sugar units are linked together through a chemical bond known as glycoside bond. This glycosidic bond makes disaccharides more complex than monosaccharides.
The disaccharides are two types, reducing disaccharides (Have aldehyde or ketone group) and nonreducing disaccharides (No aldehyde or ketone group). Some basic examples of disaccharides are lactose, sucrose and maltose etc.
Characteristics
- Disaccharides are made of two sugar units.
- They are crystalline.
- They are sweet in taste but not so then monosaccharides.
- Broken down into monosaccharides before absorption.
- Single glycosidic bond present between the sugar units or monosaccharides.
What are polysaccharides in Biochemistry?
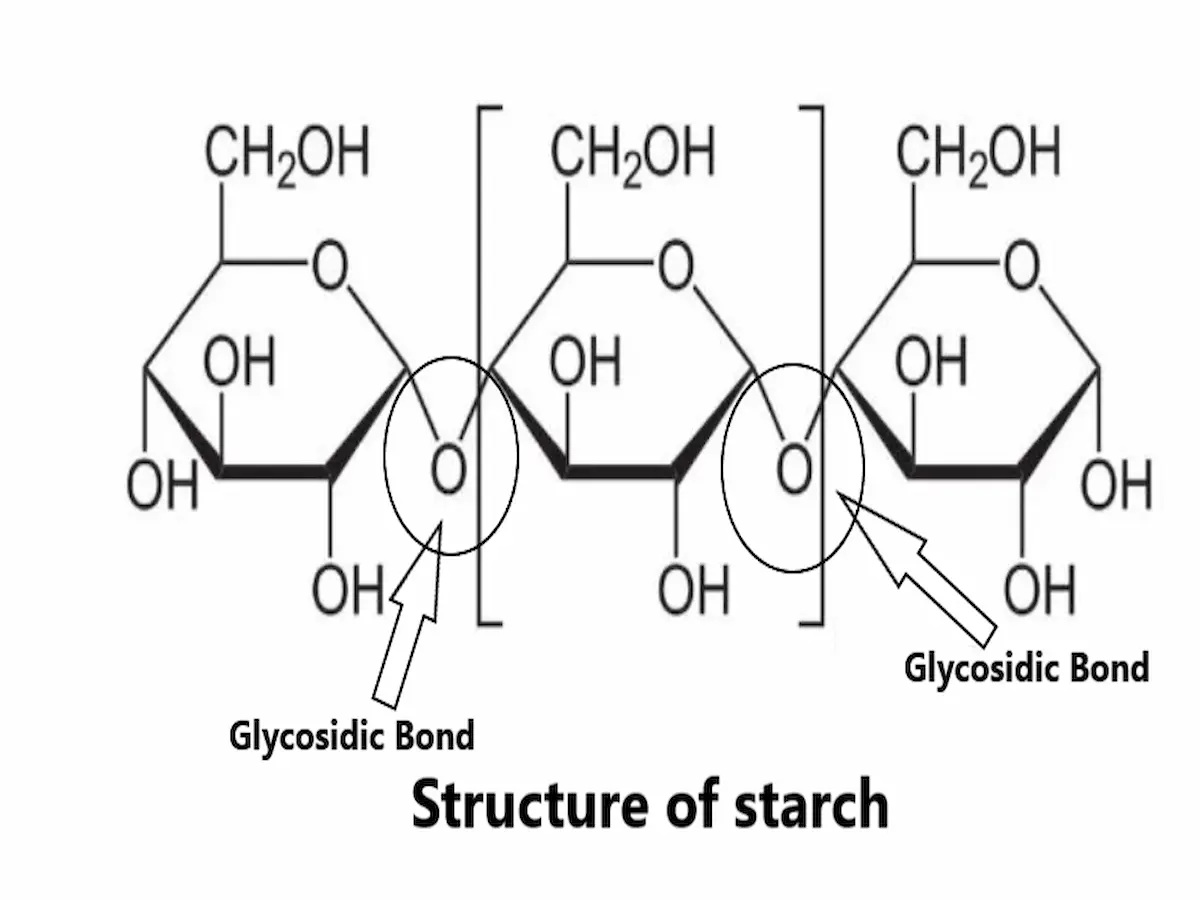
We all know poly means many and saccharides means sugar. So, in biochemistry polysaccharides are a category of carbohydrate made of multiple sugar molecules or monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides are linear as well as branched polymers of monosaccharides. These are also known as complex carbohydrate because of the complex structure and long chains of monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides are two types homopolysaccharides (single type of monosaccharides) and heteropolysaccharides (Mixture of monosaccharides). Some examples of polysaccharides are starch, glycogen and cellulose.
Characteristics
- These are composed of many sugar units.
- Generally, not sweet in taste.
- They form colloids with water or insoluble in water.
- Polysaccharides broken down slowly and that’s why they provide sustain release of energy.
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and Polysaccharides: Which is better for our body?
By understanding the differences between the monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides we can know about dietary choices. Simple sugars like monosaccharides and disaccharides provide quick energy but can increase blood sugar levels. But polysaccharides offer a slower and sustained energy release, which is better for long-term health and energy management.
Also read Carbohydrates vs proteins vs lipids vs nucleic acids.

