Learn what are proteins, classifications and functions. The term protein derived from a Greek word “proteios”.
These are the large macromolecule contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur and composed of many units of amino acid. In shortly, proteins are the polymer of amino acid.
There are 20 different types of amino acid, which are attached together to make a protein.
Recently 21st amino acid is discovered which is selenocysteine.
Who discovered proteins?
In 1838, a Swedish chemist Jons Jacob Berzelius used the term protein to some organic compound.
What are amino acids?
Amino acids are a group of organic compounds contain two functional groups – carboxyl group (-COOH) and amino group (-NH2).
Basically, carboxyl group is acidic in nature and amino group is basis in nature.
Composition of protein
Constituted by 5 major elements. Those are – carbon (50-55%), hydrogen (6-7.3%), oxygen (19-24%), nitrogen (13-19%) and sulphur (0-4%).
This biomolecule also contains other elements such as ferus, copper, iron, magnesium, zinc etc.
Nitrogen is the essential components of protein. The average presence of nitrogen in a protein is 16%.
Classification of proteins
Classified on 3 ways,
- According to structure.
- Based on shape.
- According to composition.
1) According to protein structure they further classified onto 4 categories – primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein.
What is primary protein?
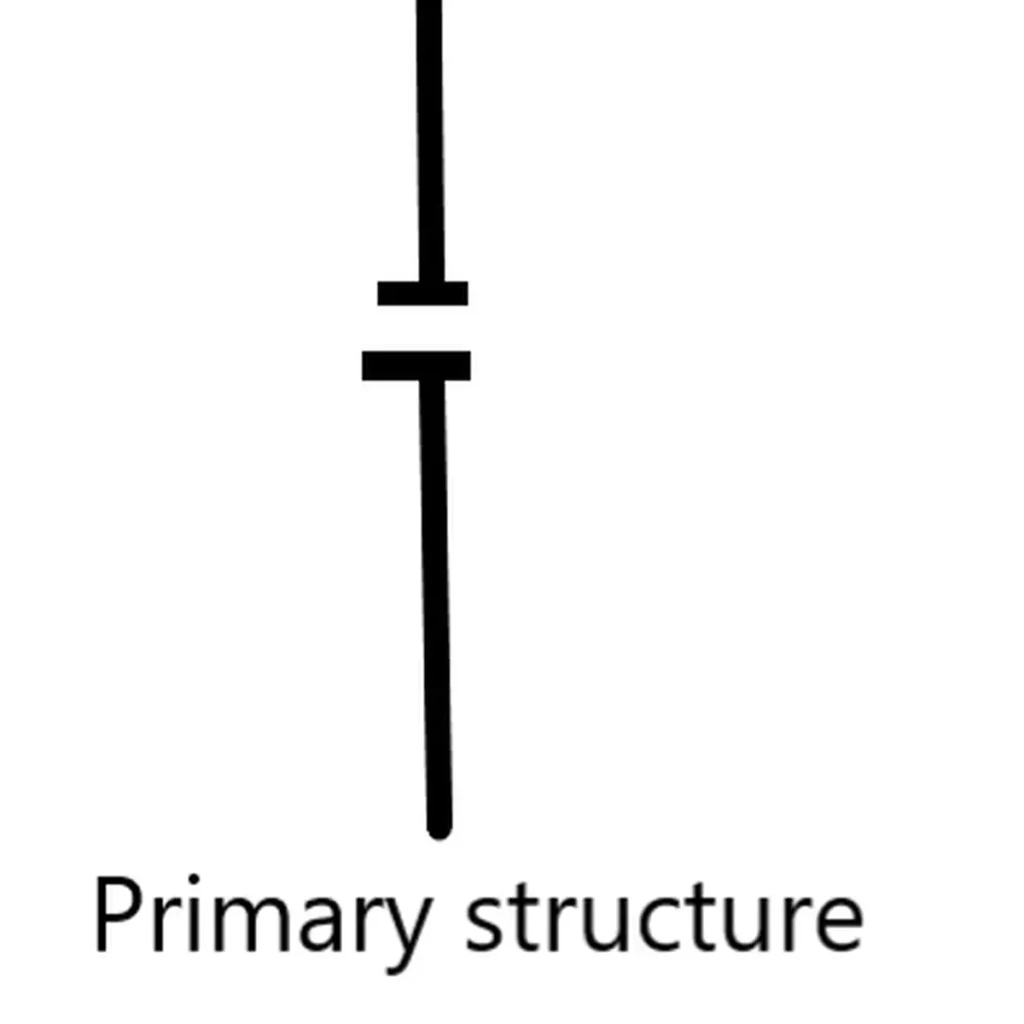
It represents the linear sequence of amino acid in a chain.
What is secondary protein?
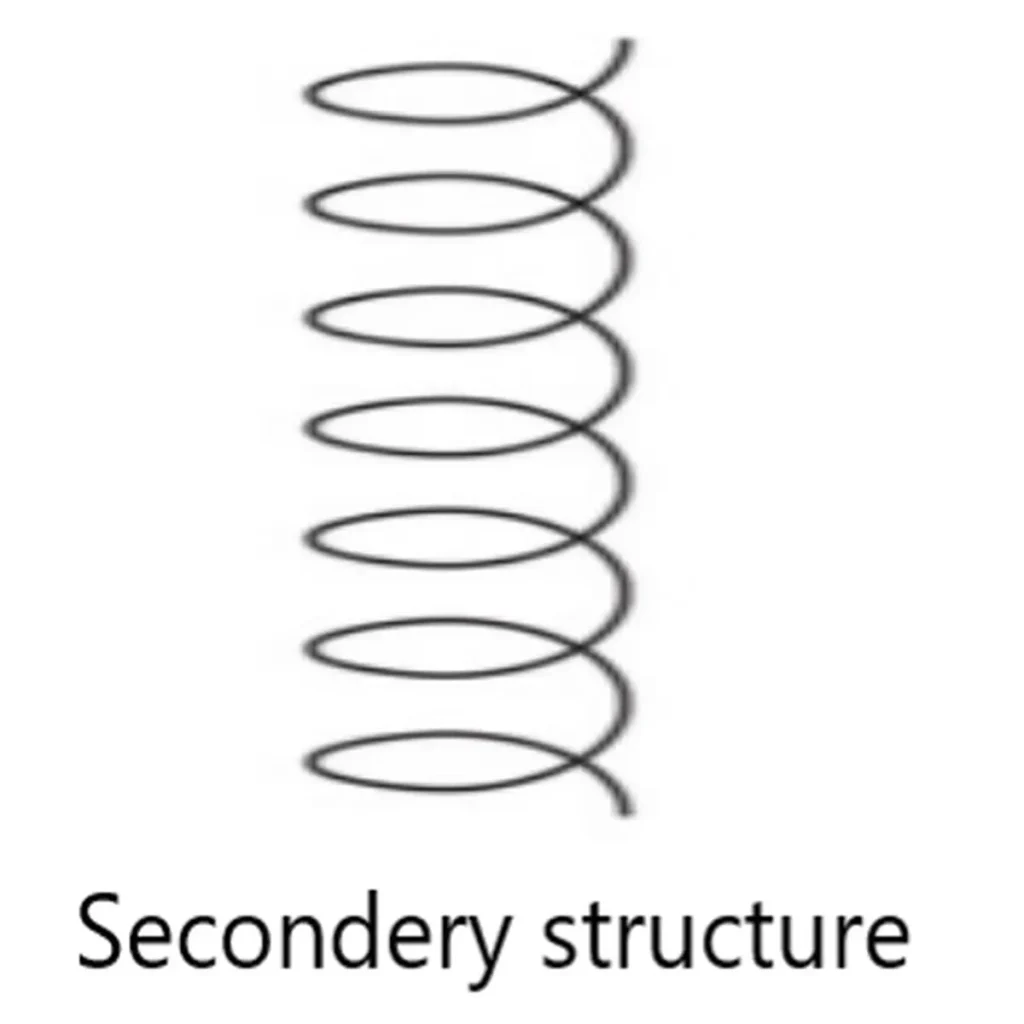
It is the spatial arrangement of protein where amino acid are twisted and folded in chain.
What is tertiary protein?
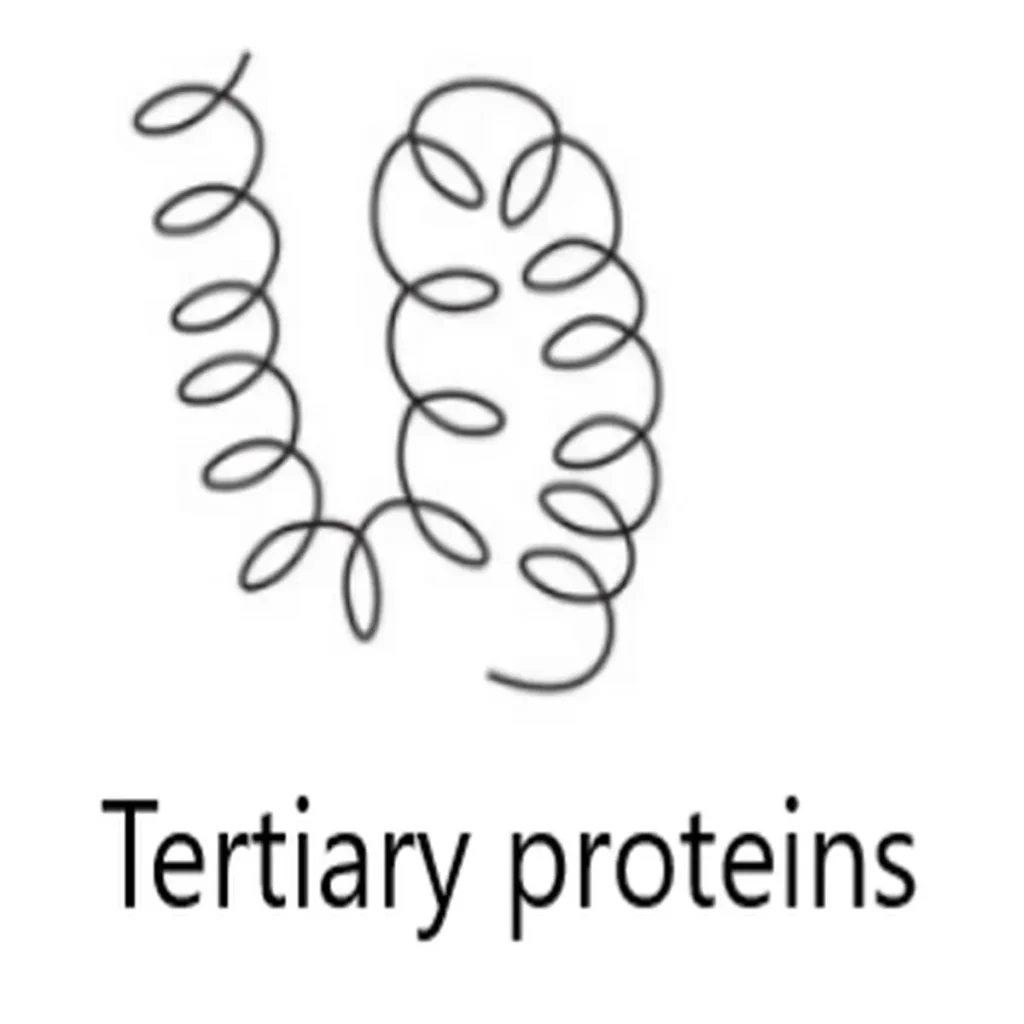
It is three-dimensional (3d) structure protein. Here proteins are bended and arranged or incorporated into specific loop.
What is quaternary protein?
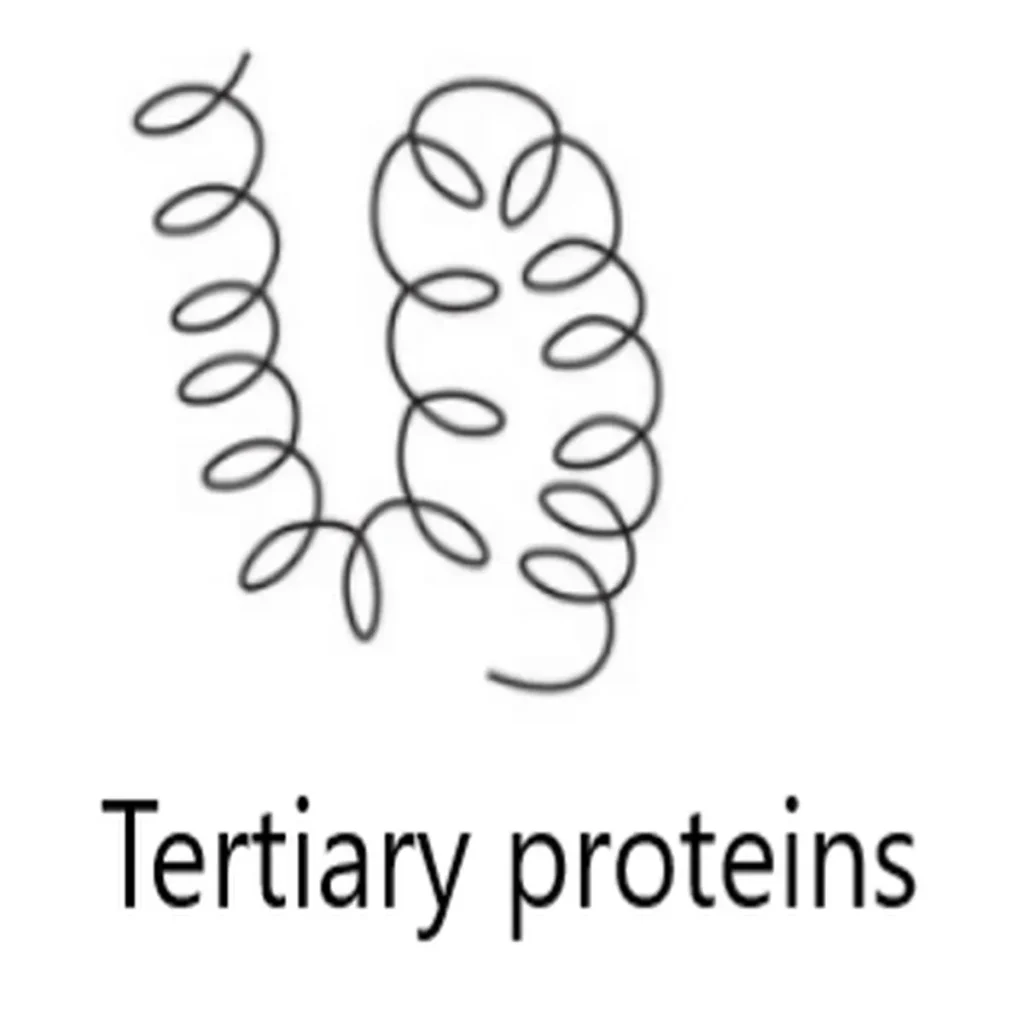
When the protein structure consisting of more than one folded amino acid chain.
2) On the basis of shape proteins are subdivided into fibrous and globular proteins.
What are fibrous proteins?
These are fibrous in nature and insoluble in water. Fibrous proteins are the long linear chain of protein held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Hydrolytic proteolytic enzyme is not able to digest these. For example, collagen (skin), keratins (hair), elastin (arteries and tendon).
What are globular proteins?
These are spherical or oval shaped and soluble in water. These are digestible. For example, albumins, globulins, histones etc.
3) On the basis of composition, proteins are subdivided into 3 types – simple, conjugated and derived proteins.
What is simple protein?
When the protein made-up of only by amino acids on their hydrolysis. For example, albumin, globulin etc.
What is conjugated protein?
This is also known as complex protein. Here protein molecules are combined with the non-protein or non-amino acid group. This non-protein or non-amino acid group is called as prosthetic group. Some examples are, nucleoproteins, glycoproteins, lipopropteins etc.
What is derived protein?
When a protein is hydrolyzed by acid, alkalis, heat and enzymes called derived protein. For example, cooked protein (egg white), fibrin, peptones etc.
What are roles of protein?
Protein performs essential functions in living organism. These functions may be static (structural) and dynamic.
Structural function of protein
Proteins perform brick and mortar roles and are primarily responsible for structure and strength of body. For examples, collagen and elastin found in bone matrix, vascular system and other organs and α-keratin present in epidermal tissues.
Dynamic function of protein
The dynamic functions of proteins are more diversified in nature. It acts as enzymes, hormones, blood clotting factors, immunoglobulins, membrane receptors, besides their function in genetic control, muscle contraction, respiration etc. Protein is the “working horses of cell”.
What are the foods with high protein?
Here are some high protein foods,
- Eggs: One large egg gives 6.3 grams of protein.
- Almonds: One ounce of almonds provides 6 grams of protein.
- Chicken breast: One half of a chicken breast provides 26.7 grams of protein.
- Cottage cheese: One cup of cottage cheese provides 28 grams of protein.
- Greek yogurt: One cup of Greek yogurt provides 23 grams of protein.
- Lentils: One cup of cooked lentils provides 18 grams of protein.
- Lean beef: One 3-ounce serving of lean beef provides 22 grams of protein.
- Fish: A 3-ounce serving of fish provides 17 grams of protein.
- Quinoa: One cup of cooked quinoa provides 8 grams of protein.
How much protein I should eat per day?
The amount of protein for your body depends on several factors, such as your age, sex, weight, height and activity level.
According to the National Institutes of Health, the daily protein intake for an adult should be 0.36 grams per pound of body weight.
If you are physically active, you may need more protein for muscle growth and repair. Studies suggest that 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight is ideal for people who want to gain or maintain muscle mass.
Also read What are biomolecules?
