In 1844, a German chemist “Carl Schmidt” used the word carbohydrates. In 1856, a French physiologist “Claude Bernard” discovered that glycogen (a form of carbohydrate) stored in animal liver.
Carbohydrates are the most available biomolecules or macronutrients composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. These are produces after the hydrolysis of carbon.
So, they may define as the polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketones or compounds which are produced after the hydrolysis of carbon.
Carbohydrates are the essential nutrients which includes sugar, starch and fiber. All these are found in foods and drinks such as fruits, grains etc.
Actually, we know carbohydrate as sugar. This sugar word came from Greek word “Sakcharon” which mean sugar (sweet substances).
Our body convert carbohydrates to glucose. Glucose is also known as body sugar. Glucose is the main energy source of body. This can be used immediately or stored in liver or muscle for later use.
The general formula of carbohydrate is Cn(H2O)n
What are the 3 types of carbohydrates?
Based on presence of sugar unit’s carbohydrates are classified into 3 main categories – monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Scientifically, sugar units are called as saccharides.
What are monosaccharides?
“Mono” means one or single. So, when a single or one sugar unit is present it is known as monosaccharides. These are the simplest group of carbohydrate. These are also known as simple sugars.
Based on the number of functional group monosaccharides divided into different categories-Aldoses and Ketoses.
What are Aldoses?
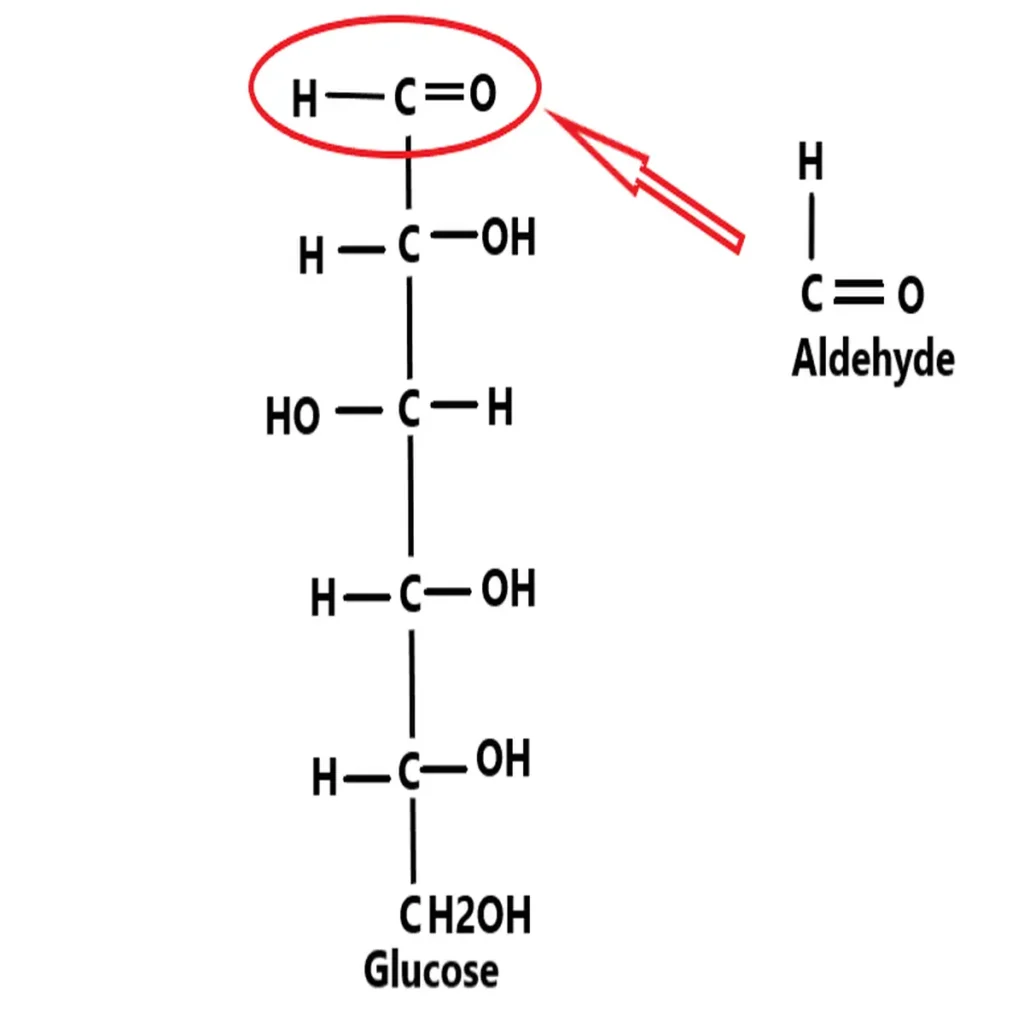
When the functional group in monosaccharides structure is aldehyde, they are called aldoses. Example- Glucose, glyceraldehyde etc.
What are ketoses?
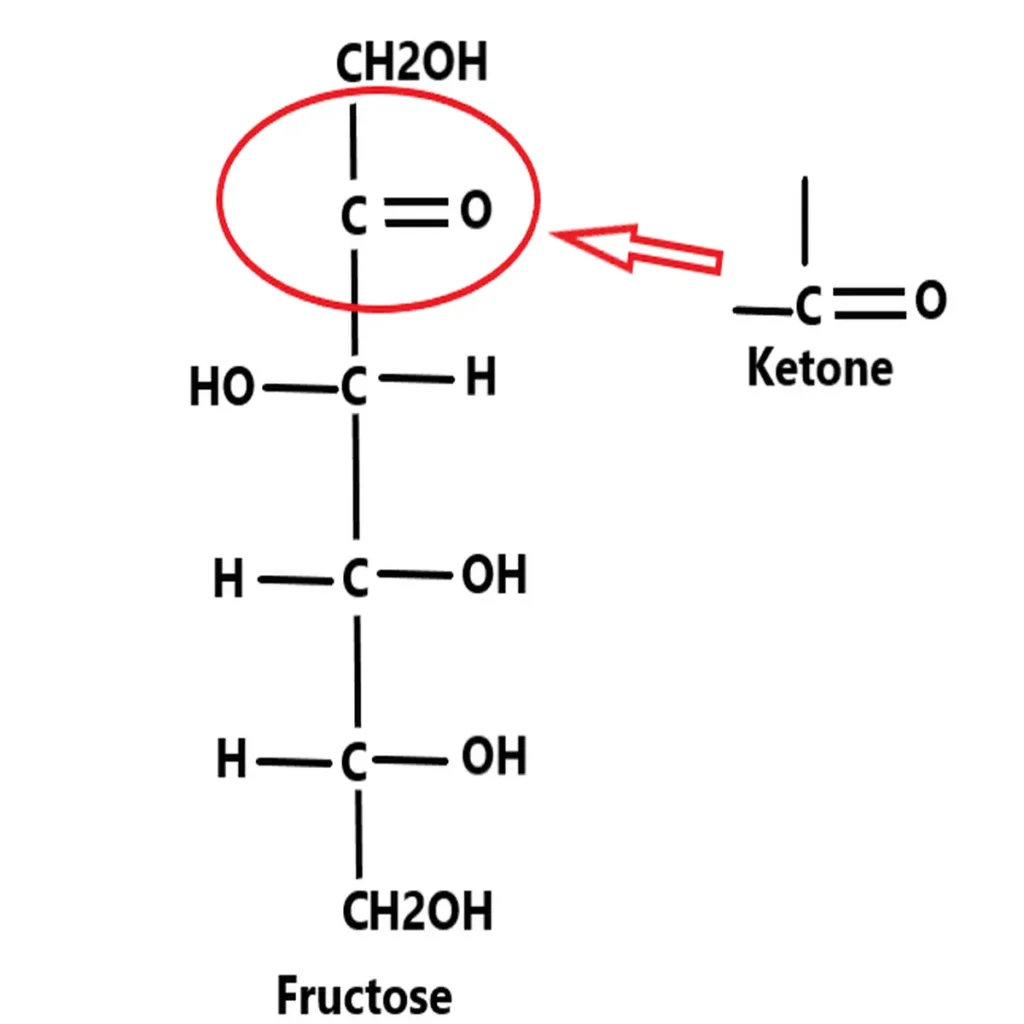
When the functional group in monosaccharides is ketones is known as ketoses. Example- fructose.
Based on the presence of carbon atoms monosaccharides are classified into – trioses (C3H6O3), tetroses (C6H6O4) pentoses (5C), hexoses(6C) and heptoses (presence of 7 carbon)
For naming of monosaccharides, we have to use term from functional group and number of carbon atoms. For example, glucose is an aldohexose. Here “Aldo” because glucose structure contains aldehyde group and “Hexose” because it contains 6 carbons atoms in structure.
What are oligosaccharides?
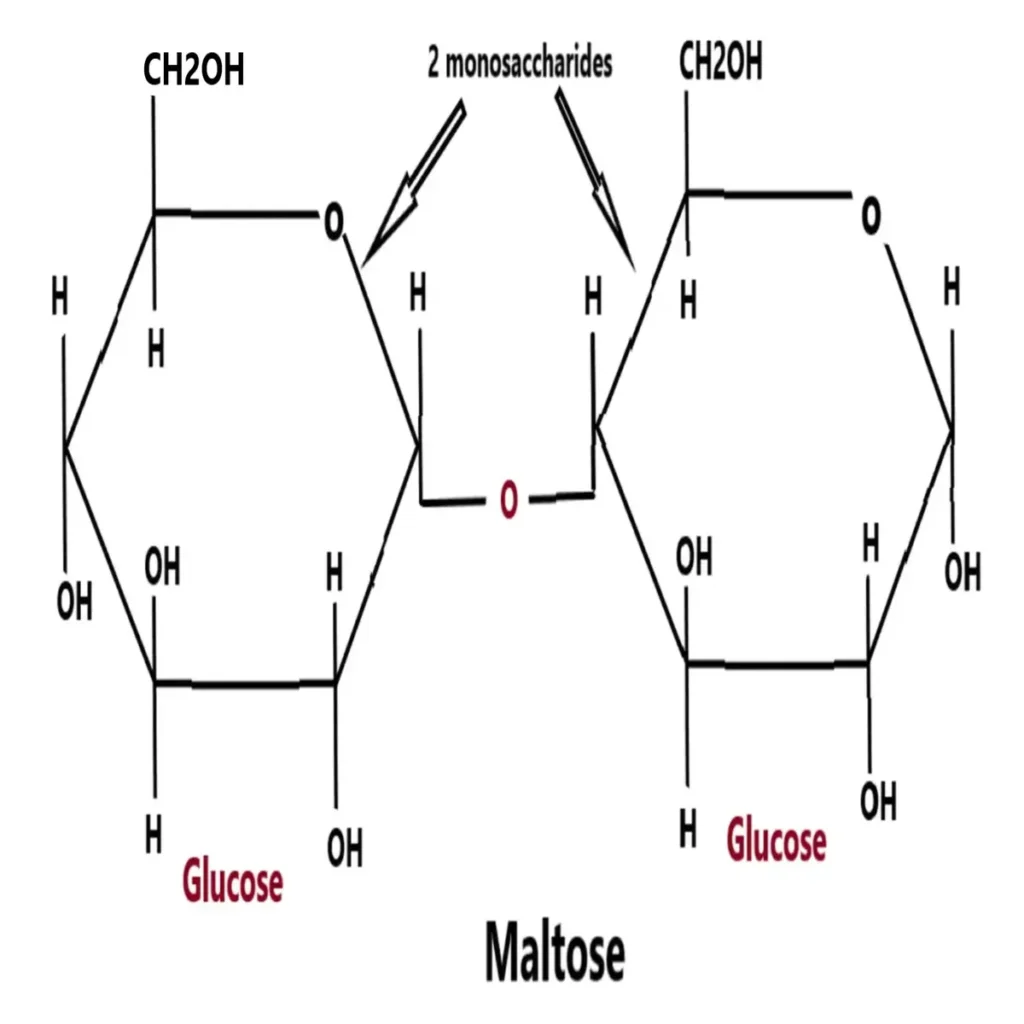
In Greek “Oligo” means few. Oligosaccharides are the class of carbohydrates contains 2-10 monosaccharides molecules.
Based on the presence of monosaccharides unit oligosaccharides are classified in – disaccharides (maltose), tetrasaccharides (glucose), pentasaccharides (verbascose), hexasaccharides, heptasaccharides and octasaccharides.
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are the polymer of multiple units of monosaccharides. They are long and linear chain of carbohydrates. Polysaccharides have high molecular weight up to 9 million. These biomolecules are the important source of energy in living organism. For examples, glycogen, cellulose, starch etc.
Polysaccharides are further subdivided to – heteropolysaccharides and homopolysaccharides.
What are heteropolysaccharides?
When the polysaccharides are composed of different types of sugar units or monosaccharides they are referred as heteropolysaccharides. These are also knowns as heteroglycans. For example, hyaluronic acid, heparin, gamma globulin etc.
What are homopolysaccharides?
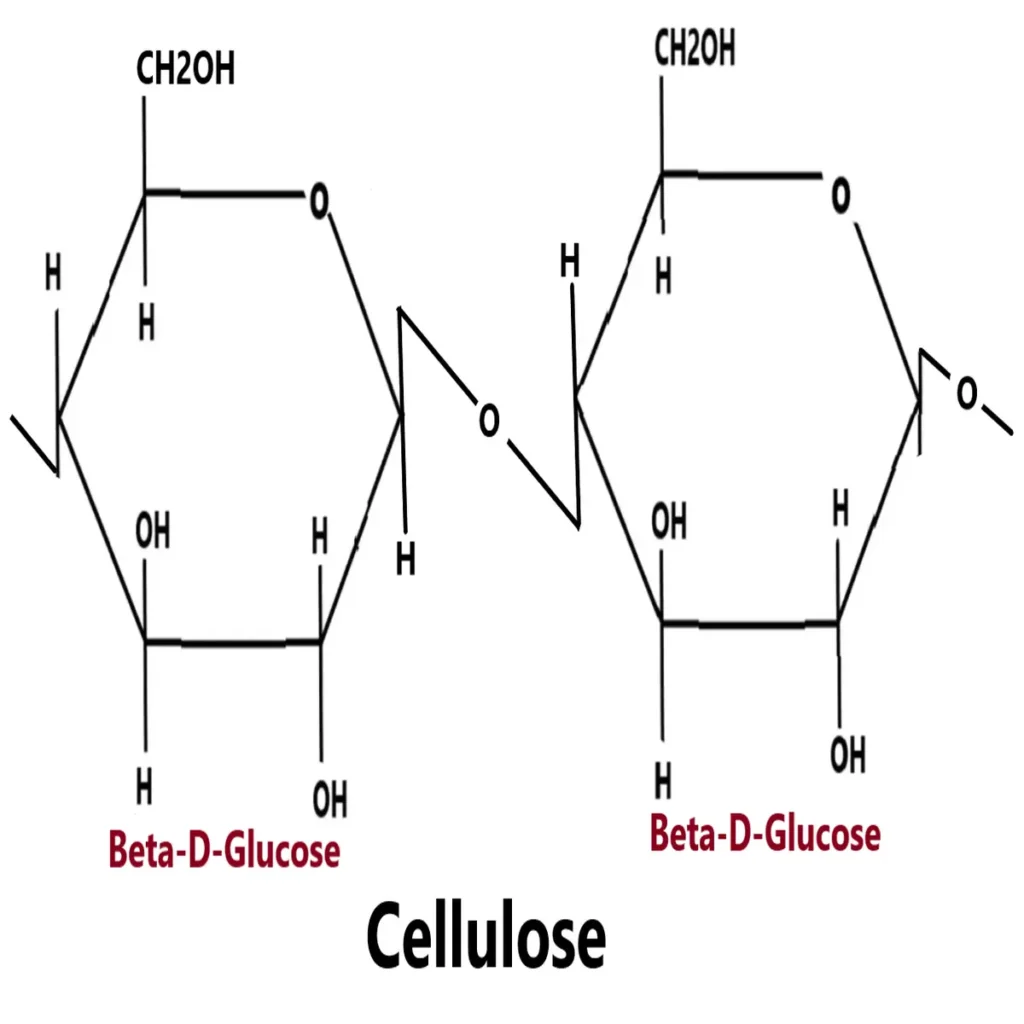
When the polysaccharides are made up of some monosaccharides, then it called homopolysaccharides. For example, glycogen, cellulose, starch, chitin etc.
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
They are the most abundant source of energy for organisms. Carbohydrates help to give the structure of cell membrane along with cell growth, adhesion, fertilization. They also store the energy as glycogen in body.
What are the examples of carbohydrates?
These are the common example of carbohydrates – glucose, galactose, maltose, fructose, chitin, starch, cellulose, sucrose, lactose etc.
What are foods with carbohydrate?
These are the common foods with carbohydrates,
- Grains (bread, noodles, pasta, crackers, cereals and rice).
- Fruits (apples, bananas, berries, mangoes, melons and oranges).
- Dairy product (milk, yogurt).
- Dried beans, lentils, peas etc.
- Snacks and sweets (cakes, cookies, candy, desserts etc.)
Which type of carbohydrate should I eat?
Eat whole grain, do not eat refined grain. Here whole grain means breads, brown rice, whole rice etc. Eat foods with fiber like fruits. Do not eat foods with lot of added of sugar.
Also read What are biomolecules? What is Biochemistry?
FAQ’s
What is the monomer for carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates monomer known as monosaccharides. These simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose.
What do carbohydrates do?
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for living organisms.
How to classify the sugars as either aldoses or ketoses?
If the sugars contain aldehyde functional groups (-CHO) are classified as aldoses (e.g., glucose). On other hand if the sugar contain ketone functional groups (C=O) are classified as ketoses (e.g., fructose).
What is main difference between aldoses and ketoses?
Aldoses have an aldehyde functional group (-CHO) on the carbon chain, but ketoses have a ketone functional group (C=O) within the carbon chain.
What is the main difference between the heteropolysaccharides and homopolysaccharides?
Homopolysaccharides consist of a single type of monosaccharide, while heteropolysaccharides contain multiple types of monosaccharides in their polymer chain.
Does microorganism contains carbohydrates?
Yes, microorganisms contain carbohydrates. One example of carbohydrates in microorganisms is the bacterial cell wall which is made up of peptidoglycan.
Who discovered glycogen?
In 1856, a French physiologist “Claude Bernard” discovered that glycogen. He finds out that glycogen stored in animal liver.
What is the main difference between monosaccharides and disaccharides?
Monosaccharides are single sugar units, but disaccharides contain two monosaccharide units.
Also read Classification of carbohydrates.
