Learn what are the differences between lipids vs proteins in biochemistry. Learn their definition and functions.
What are lipids?
Lipids are the organic and heterogenous compounds relatively insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents (alcohol, ether). These are mostly small molecules and do not have polymer like proteins and carbohydrates.
Lipids are classified into simple (fats and oils), complex (phospholipids, glycolipids), derived (fatty acids, steroid hormones) and miscellaneous lipids (carotenoids). Fatty acids are the major constituents of various lipids.
They play crucial roles in various biological processes and are an essential component of living cells.
Functions of lipids
- Lipids store energy as triacylglycerols.
- They form cell membranes.
- Lipids provide fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K).
- They regulate metabolism with hormones.
- Lipids protect organs and give shape to the body.
What are proteins?
Proteins are nitrogen containing, most abundant organic macromolecules present in animals and plants. These are polymers of amino acids.
Proteins are classified into three major groups: simple proteins, conjugated proteins and derived proteins.
Proteins occur in every part of the cell. 50% of the cellular dry weight is proteins and these form the basis of structure and function of life.
Functions of proteins
- Primarily responsible for structure and strength of body.
- Proteins act as enzymes, hormones, blood clotting factors, immunoglobulins and membrane receptors etc.
- They act as catalysts to facilitate biochemical reactions.
- Proteins contribute to movement and muscle contraction.
- Act as a store for amino acids and essential nutrients.
Lipids vs proteins
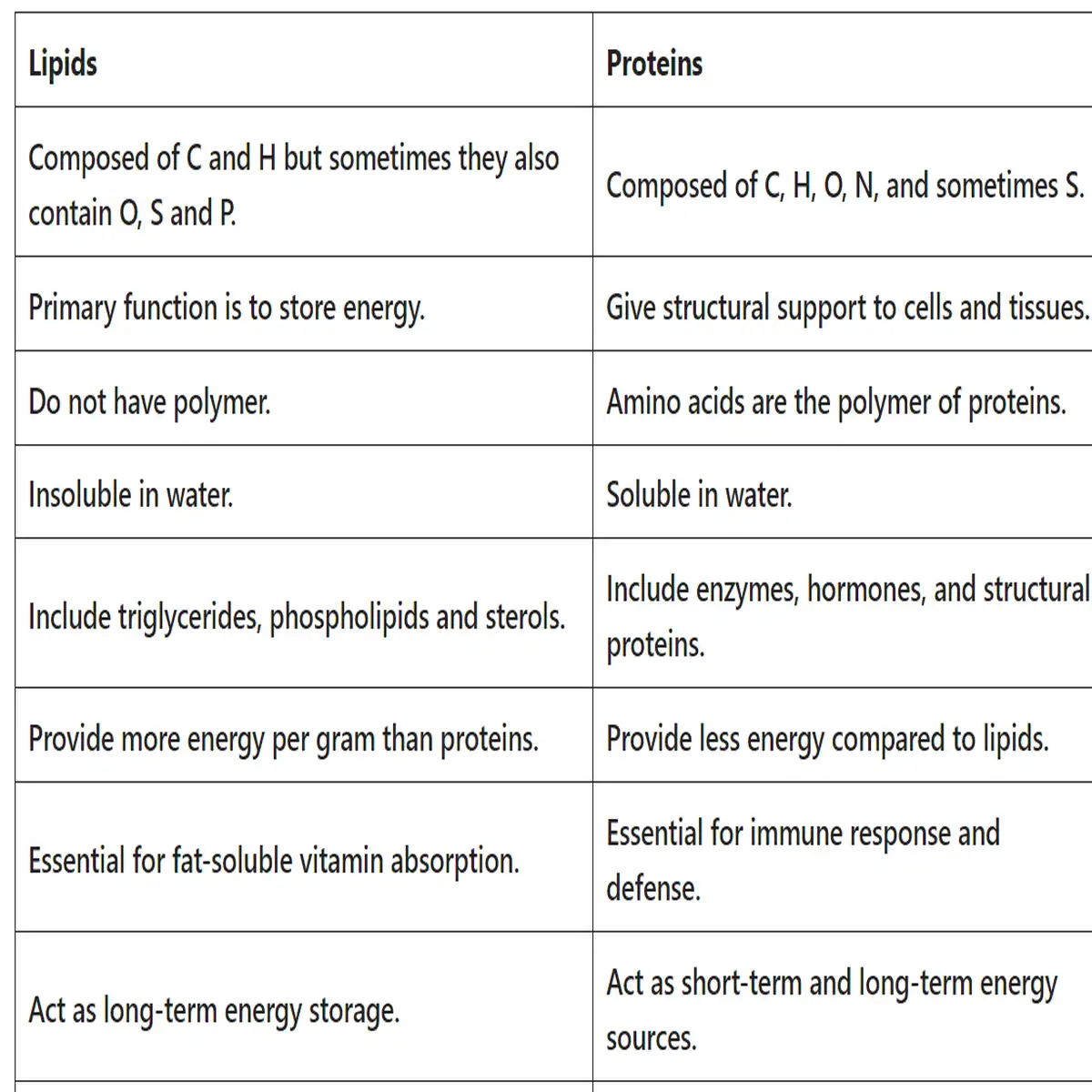
| Lipids | Proteins |
| Composed of C and H but sometimes they also contain O, S and P. | Composed of C, H, O, N, and sometimes S. |
| Primary function is to store energy. | Give structural support to cells and tissues. |
| Do not have polymer. | Amino acids are the polymer of proteins. |
| Insoluble in water. | Soluble in water. |
| Include triglycerides, phospholipids and sterols. | Include enzymes, hormones, and structural proteins. |
| Provide more energy per gram than proteins. | Provide less energy compared to lipids. |
| Essential for fat-soluble vitamin absorption. | Essential for immune response and defense. |
| Act as long-term energy storage. | Act as short-term and long-term energy sources. |
| Involved in hormone production. | Act as enzymes in metabolic pathways. |
| Found in adipose tissue and cell membranes. | Present throughout all cellular structures. |
| These are non-polar molecules. | These have polar and non-polar regions in their structure. |
| Storage in plants in the form of oils. | Stored in muscles and tissues. |
| Can be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. | Broken down into amino acids during digestion. |
| Essential for efficient energy source. | Essential for cellular repair and maintenance. |
| Commonly found in adipocytes and adipose tissues. | Present in every cell. |
FAQ from lipids vs proteins

What do you mean by heterogenous compounds?
“Heterogeneous compounds” refer to the substances that are composed of different elements or molecules that are not uniform throughout. For example, a mixture of oil and water. It is heterogeneous because oil and water do not mix on a molecular level and they form separate layers.
Why don’t lipids have polymers?
As we know polymers are large molecules made up of repetitive subunits called monomers. Lipids do not have polymers like proteins, nucleic acids or carbohydrates because they are not typically composed of repeating monomeric units.
What is the major difference between lipids and proteins?
Lipids are composed of carbon and hydrogen also sometimes they contain oxygen, sulfur and phosphorus and are hydrophobic. But proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur. One more major difference is lipids do not have any polymers, but proteins have polymers called amino acids.
Are lipids and fats same?
According to biochemistry the answer is “no”. Because lipids are a major category of organic compounds that include fats, oils, phospholipids and sterols. Fats are specifically a type of lipid. So, all fats are lipids, but all lipids are not fats.
What are simple lipids?
These are esters of fatty acids with alcohols. For example, triacylglycerols and waxes.
What are complex lipids?
These are esters of fatty acids with alcohols also contain additional groups such as phosphate, nitrogenous base, carbohydrate, protein etc. For example, lecithin, cephalin, sphingomyelin, cerebrosides etc.
What are derived lipids?
These are the compounds derived from the hydrolysis or chemical modification of complex lipids. For example, glycerol and other alcohols, fatty acids, mono-and diacylglycerols, steroid hormones etc.
What are miscellaneous lipids?
These are a large number of compounds with the characteristics of lipids, but they don’t fit neatly into the categories of simple or complex lipids. For example, carotenoids, squalene etc.
Also read, What are lipids?