Learn about what are the differences between carbohydrates vs proteins. Explore with its definition and functions.
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients. It is a significant portion of the human diet. They are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Carbohydrate literally means ‘hydrates of carbon’. Carbohydrates act as a primary source of energy for the body. These are crucial for various physiological functions.
Carbohydrates are broadly classified into three major groups – monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Functions of carbohydrates
They are the most abundant dietary source of energy (4Cal/g) for all organisms.
Carbohydrates are precursors for many organic compounds (fats, amino acids).
Glycoproteins and glycolipids, containing carbohydrates, contribute to cell membrane structure and functions like adhesion and fertilization.
It acts as structural elements in organisms, with examples like cellulose in plant cell walls and chitin in insect exoskeletons.
Carbohydrates also serve as the storage form of energy (glycogen) to meet the immediate energy demands of the body.
What are proteins?
These are macromolecules composed of amino acids. These play a crucial role in the structure, function, and regulation of the body tissues and organs. They are one of the three main macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and fats.
Proteins are the most abundant organic compounds and constitute a major part of the body dry weight (10–12 kg in adults).
Proteins are classified in several ways. Three major types of classifying proteins based on their function, chemical nature and solubility properties and nutritional importance.
Functions of proteins
Proteins help to formation of cell structure and function. Enzymes, hormones, and immunoglobulins are examples of vital proteins.
Proteins contribute to osmotic balance, blood clotting and muscle contraction.
In starvation, amino acids from proteins become a key energy source. And some proteins act as emergency energy stores, unlike lipids and carbohydrates.
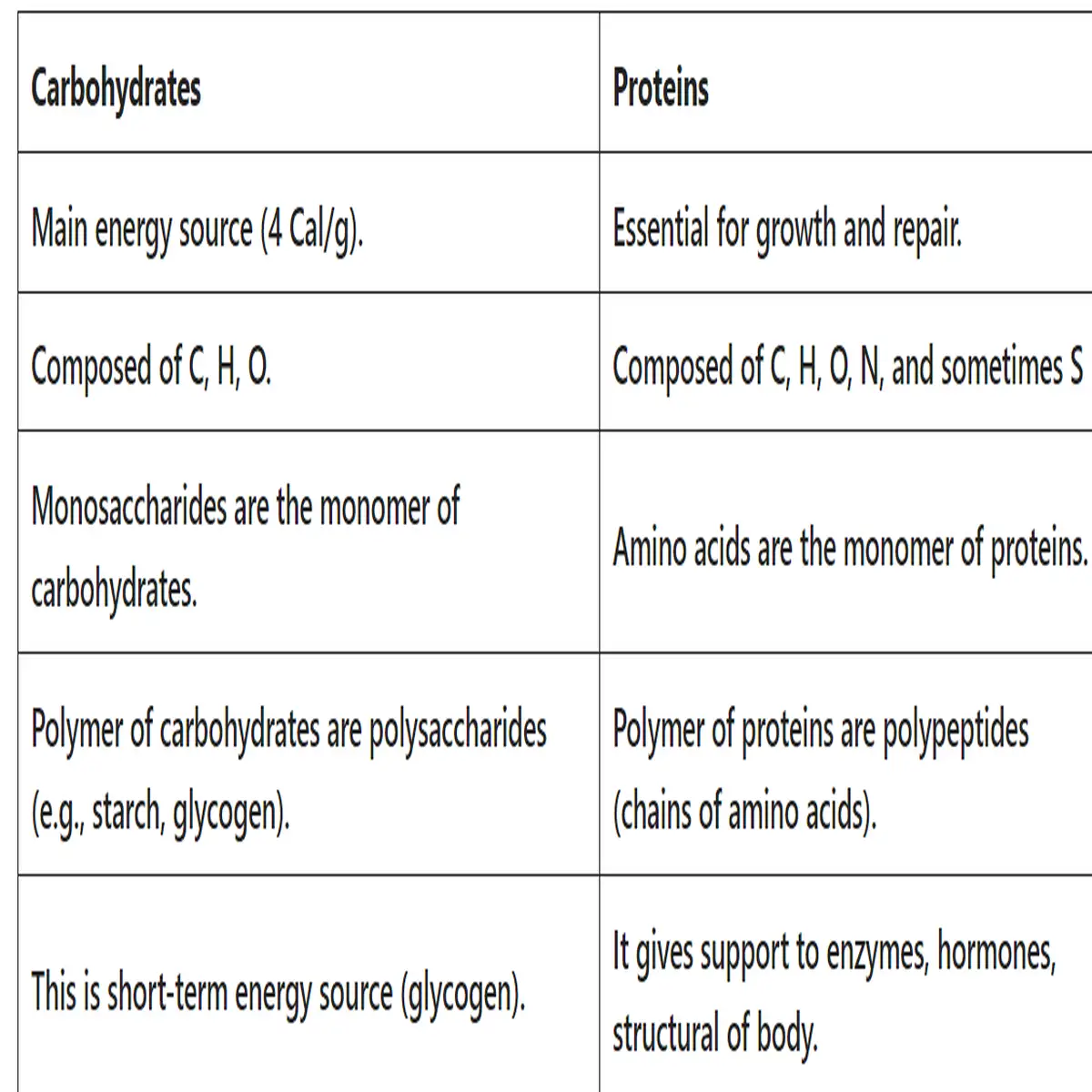
Carbohydrates vs proteins
| Carbohydrates | Proteins |
| Main energy source (4 Cal/g). | Essential for growth and repair. |
| Composed of C, H, O. | Composed of C, H, O, N, and sometimes S |
| Monosaccharides are the monomer of carbohydrates. | Amino acids are the monomer of proteins. |
| Polymer of carbohydrates are polysaccharides (e.g., starch, glycogen). | Polymer of proteins are polypeptides (chains of amino acids). |
| This is short-term energy source (glycogen). | It gives support to enzymes, hormones, structural of body. |
| Quick energy release. | Slower and sustained energy release. |
| Broken down to glucose in digestion. | Broken down to amino acids in digestion. |
| Examples: Glucose, starch, cellulose etc. | Examples: Hemoglobin, insulin, collagen etc. |
| Essential for brain function. | Essential for tissue repair and immune system. |
| Supports cell structure (glycoproteins, glycolipids). | Involved in cell signaling and regulation. |
| Storage form of carbohydrate is glycogen (in liver, muscles). | No significant storage form in the body. |
| Broken down to release ATP. | Broken down for energy and tissue building. |
| Found in fruits, vegetables, grains. | Found in meat, eggs, dairy, legumes. |
| Supports to make plant cell walls (cellulose). | Supports to make muscle structure and function. |
| It metabolized quickly. | Metabolism of proteins takes more time. |
| Provides quick energy during exercise. | Takes long time to release energy during exercise. |
FAQ
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates, often referred to as single sugar. They have the general formula Cn(H2O)n. They are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Example of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose.
What are oligosaccharides?
Oligosaccharides (Greek oligo means few) contain 2–10 monosaccharide molecules which are liberated on hydrolysis. Based on the number of monosaccharide units present, the oligosaccharides are further subdivided to disaccharides, trisaccharide etc. Example of oligosaccharides is sucrose. Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of two monosaccharide units, glucose and fructose.
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides (Greek: poly-many) are polymers of monosaccharide units with high molecular weight (up to a million). They are usually tasteless (non-sugars) and form colloids with water. The polysaccharides are of two types – homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharide. An example of a polysaccharide is starch.
What are glycoproteins?
Several proteins are covalently bound to carbohydrates which are referred to as glycoproteins. Examples includes collagen, hydrolases, proteases etc.
What are glycolipids?
Glycolipids are molecules consisting of a lipid (fat or lipid-like component) linked to one or more carbohydrate chains. Glycolipids or glycosphingolipids are important constituents of cell membrane and nervous tissues (particularly the brain). Cerebrosides are the simplest form of glycolipids. They contain a ceramide (sphingosine attached to a fatty acid) and one or more sugars.
What is glycogen?
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals, as is starch in plants. It is stored mostly in liver (6–8%) and muscle (1-2%). It is a polysaccharide composed of many glucose molecules linked together.
What is the major difference between carbohydrates and proteins?
The key difference between carbohydrates vs proteins lies in their composition and functions. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and act as primarily as a source of energy. Proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur, and they play diverse roles, including in body structure, enzymes and immune function.
What are foods with high carbohydrates?

- Vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, carrots and sweet potatoes.
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, oranges and berries.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils and chickpeas.
- Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats and whole wheat bread.
What are the foods with high proteins?

- Meat and Poultry: Chicken, turkey and beef.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, cheese and cottage cheese.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, cod and tilapia.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, peanuts, chia seeds and sunflower seeds.
- Eggs: Eggs are a complete protein source.
Also read What are carbohydrates?